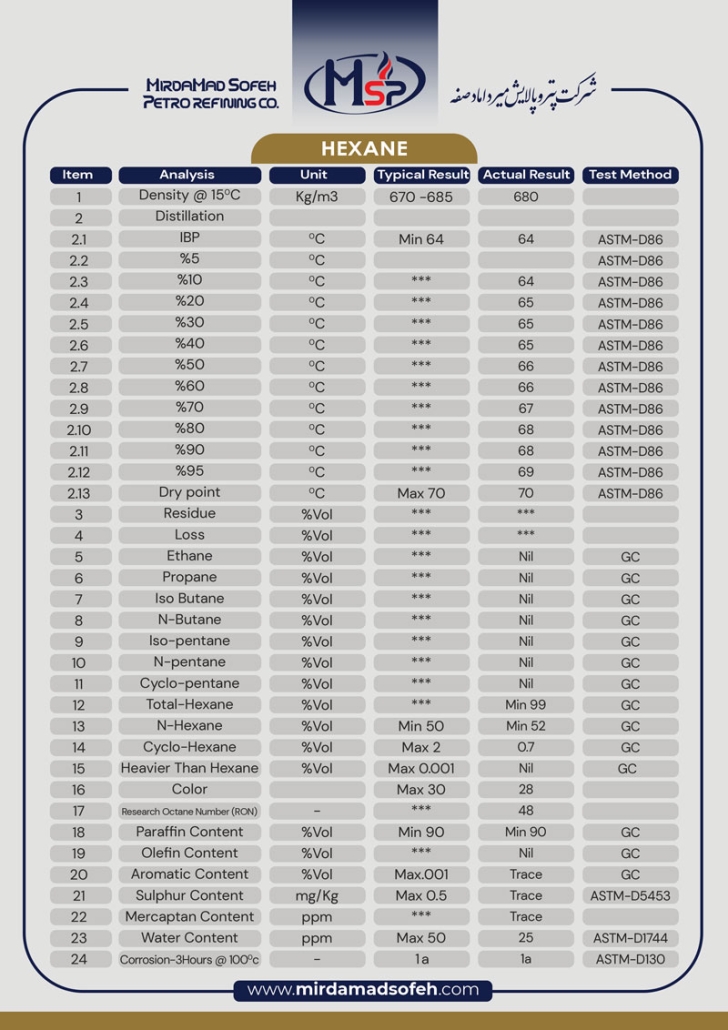
Hexane
Hexane is a chemical substance derived from crude oil. It’s a colorless liquid with an unpleasant smell. It evaporates easily in the air and only dissolves a little in water.
Hexane is a chemical compound that consists of six carbon atoms. This compound is arranged in a hexagonal structure. Hexane can exist in various chemical compounds, including hydrocarbons, alcohols, and aldehydes.
Common names for these solvents are commercial hexane, mixed hexanes, petroleum ether, and mineral spirits. The main use of hexane-containing solvents is to extract vegetable oils from products like soybeans, cotton, peanuts, and safflower seeds.
This product is also used as a cleaner in the textile, furniture, shoemaking, and printing industries, especially in rotogravure printing.
Moreover, this substance is highly flammable, and its vapors can be explosive. Heat, sparks, and flames can ignite it. Flammable vapors may leak out.
Characteristics:
Physical state: Hexane is a colorless, odorless liquid. It remains liquid at room temperature and has a specific density.
Solubility: Hexane acts as a medium solvent and can dissolve various materials. This property makes it a suitable solvent in chemistry.
Reactivity: Hexane is known as a compound with moderate reactivity. It may participate in various chemical reactions and exhibit different reactivities.
Molecular structure: Hexane has a hexagonal molecular structure that contains six carbon atoms. This molecular structure may give specific properties to this chemical compound.
These chemical properties can be very useful in examining and utilizing hexane in various industries such as chemicals, pharmaceuticals, and plastics.