LPG
Physical and Chemical Properties of LPG
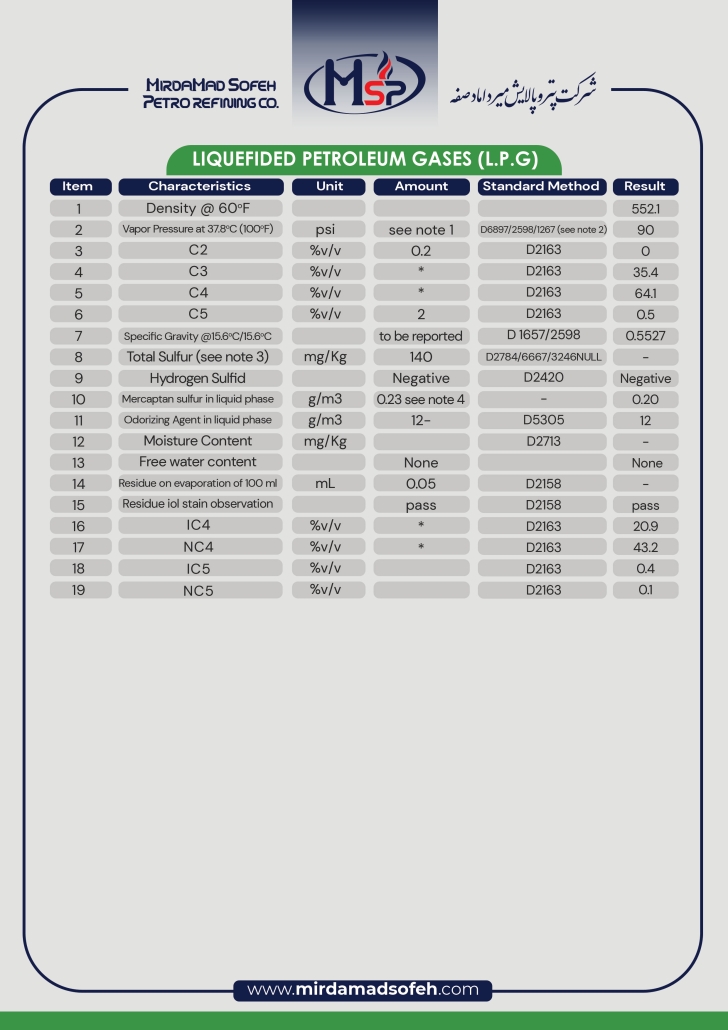
Liquefied Petroleum Gas (LPG) is a mixture of light hydrocarbons, mainly propane (C3H8) and butane (C4H10), with small amounts of propylene and butylene. This gas liquefies at the appropriate pressure and temperature. Its key properties are:
1. Flash Point: The flash point of LPG due to the combination of propane and butane is usually between -104°C (for propane) and -60°C (for butane). This property indicates its high flammability and requires caution in storage and use.
2. Boiling Point: The boiling point of propane is about -42°C and butane is about -0.5°C. Under a pressure of 8 to 13 atmospheres, LPG liquefies, which makes it easy to transport and store.
3. Solubility: Due to its non-polar hydrocarbon structure, LPG is soluble in non-polar solvents such as gasoline and oils, but has very low solubility in water. This property makes it suitable for industrial and cleaning applications.
4. Oxidation resistance: LPG has a high resistance to oxidation due to the lack of double bonds or chemically active groups. This property allows for long-term stability in storage tanks, especially in high-oxygen environments.
5. Density and calorific value: The density of LPG in the liquid state is between 0.5 and 0.58 kg/l (less than gasoline). Its calorific value is about 46.1 megajoules/kg, which is higher than gasoline (43.5 megajoules/kg) and indicates its high energy efficiency.
Safety tips:
– Proper ventilation: Use LPG in well-ventilated areas, as it is heavier than air and accumulates in low places, which can cause an explosion or suffocation hazard.
– Protective equipment: Wear gloves and safety glasses when working with tanks.
– Keep away from flames: Due to its high flammability, avoid using it near sources of sparks or flames.
– Storage: Store tanks in a cool, dry place away from heat sources with reflective paint (white or aluminum).
How to use:
– For domestic use, connect cylinders to a stove or heater with standard fittings and check for leaks with soap suds.
– In vehicles, use standard conversion systems and special refueling nozzles.
– For industrial applications, large tanks should be fitted with safety valves and automatic shut-off systems.
User hygiene:
– If inhaled, move person to fresh air and seek medical attention if necessary.
– If liquid comes into contact with skin, wash area with warm water as frostbite may occur.
– Sulfur compounds (mercaptans) are used to detect leaks, which produce a strong odor.
Comparison with similar products
LPG is compared to other fuels and solvents such as gasoline, diesel, CNG and petroleum solvents (such as Solvent 400):
1. Compared to gasoline:
– Advantages: lower emissions (52% reduction in particulate matter and 21% reduction in NOx), higher calorific value, and lower cost in some areas.
– Disadvantages: lower volumetric energy density (26 MJ/L vs. 34 MJ/L for gasoline), need for pressurized tanks.
2. Compared to CNG:
– Advantages: 3-4 times higher calorific value, easier transportation as a liquid, and better power and acceleration in cars.
– Disadvantages: Less refueling infrastructure in some countries, and higher price in the absence of subsidies.
3. Compared to Solvent 400:
– Advantages: Wider application as a fuel and propellant, and lower emissions compared to heavy petroleum solvents.
– Disadvantages: Solvent 400 is more specialized for cleaning and dilution, while LPG is used more for energy and heating.
Test results and user experiences
1. Test results:
– Refinery tests show that LPG, with its very low sulfur content (0.006%), is a cleaner fuel than gasoline and diesel.
– Tests of LPG-fueled vehicles in Europe show a 40-60% reduction in CO and SO2 emissions and an increase in engine life due to the absence of oil washing the cylinder walls.
– In domestic applications, high-octane LPG (RON=105) has better thermal efficiency than traditional liquid fuels.
2. User Experiences:
– Domestic users in India and Iran have reported that LPG is faster and more economical for cooking than coal or kerosene.
– Drivers of LPG-powered vehicles in Turkey and Italy are satisfied with the reduced fuel costs and smooth engine performance, but have noted the lack of refueling stations in some areas.
– In small industries, the use of 50 kg cylinders has been welcomed due to their easy portability and installation.
Conclusion
Liquefied petroleum gas (LPG) is a versatile fuel and industrial material due to its unique physical and chemical properties, including high calorific value, low emissions, and easy portability. Its wide applications in heating, automotive, and chemical industries, along with its high safety when standards are met, make it an attractive option compared to gasoline, CNG, and petroleum solvents such as Solvent 400. For purchase and use, it is essential to pay attention to standards, storage conditions, and choosing reputable suppliers.
You can contact Mirdamad Sofeh Petrorefinery Company to purchase liquefied petroleum gas or LPG to receive product samples.