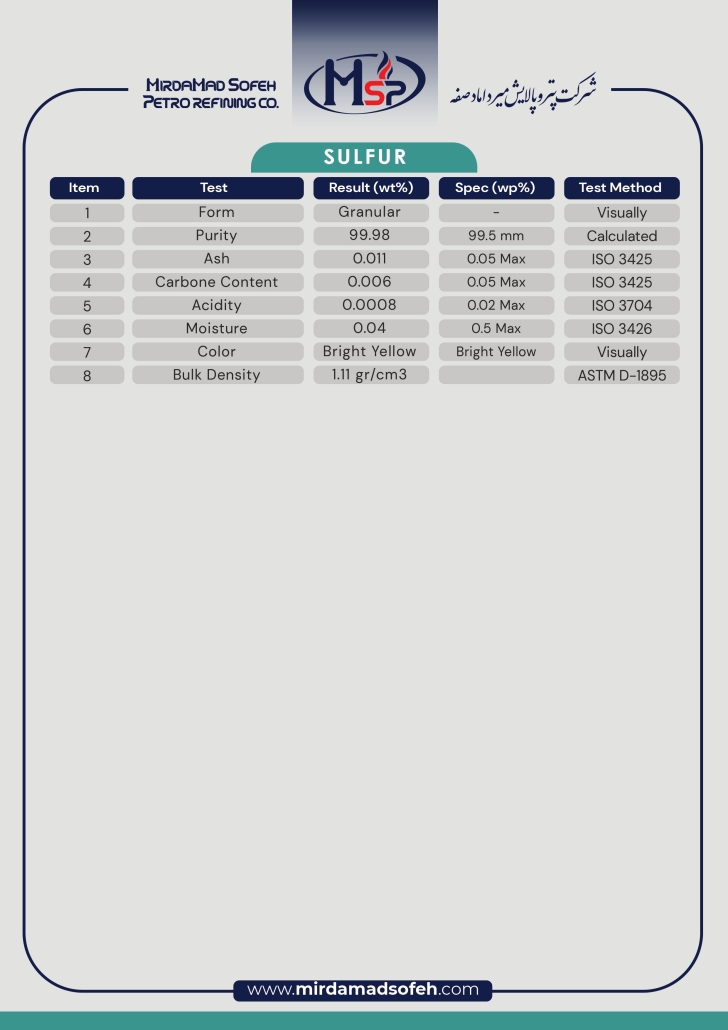
Sulfur
Sulfur is a nonmetallic element with the chemical symbol S and atomic number 16 that occurs naturally as a light yellow, odorless, brittle crystalline solid. This element has a wide range of uses in various industries due to its unique chemical and physical properties, including polymorphism (allotropy) and high reactivity. Sulfur is commonly found as an element near volcanoes and hot springs or is extracted as a byproduct of oil and gas refining processes. The name sulfur is known in ancient texts as “brumstone” (burning stone) and has been associated with fire and burning in many cultures.
Physical and Chemical Properties
Flash Point:
Solid sulfur does not have a flash point on its own, but when burned in the presence of oxygen, it produces a blue flame and releases dioxide (SO2). The ignition temperature of sulfur powder is about 190 ° C, which indicates its high flammability under certain conditions.
Boiling Point:
The boiling point of sulfur at standard pressure is 444.6 ° C. This property allows sulfur to be converted into steam in industrial processes.
Solubility:
It is insoluble in water but dissolves well in organic solvents such as carbon disulfide (CS2) and benzene. This property is used in sulfur purification and extraction processes.
Oxidation Resistance:
Sulfur is stable under normal conditions and resists oxidation. However, in the presence of oxygen and high temperatures, it oxidizes rapidly and produces compounds such as sulfur dioxide (SO2) or sulfur trioxide (SO3).
Instructions for use
Storage:
should be stored in a dry, cool environment away from sources of ignition or heat. Warehouses should be well ventilated to prevent the accumulation of toxic gases such as H2S.
Safe use:
Avoid prolonged skin contact and inhalation of sulfur dust, as it may cause skin irritation or respiratory problems.
Wear protective equipment such as gloves, masks, and goggles when working with sulfur.
Be aware that sulfur dioxide (SO2), a toxic gas, is produced when burns.
User hygiene:
In case of skin contact, wash the area with soap and water.
Inhaling large amounts of sulfur dioxide or hydrogen sulfide can cause respiratory irritation or even severe poisoning.
Emergency measures:
In case of fire, use CO2 or dry powder extinguishers. If toxic gases are inhaled, move the person to fresh air and seek medical attention immediately.
To purchase and order, contact the sales experts of Mirdamad Sofeh Petrorefining Company.